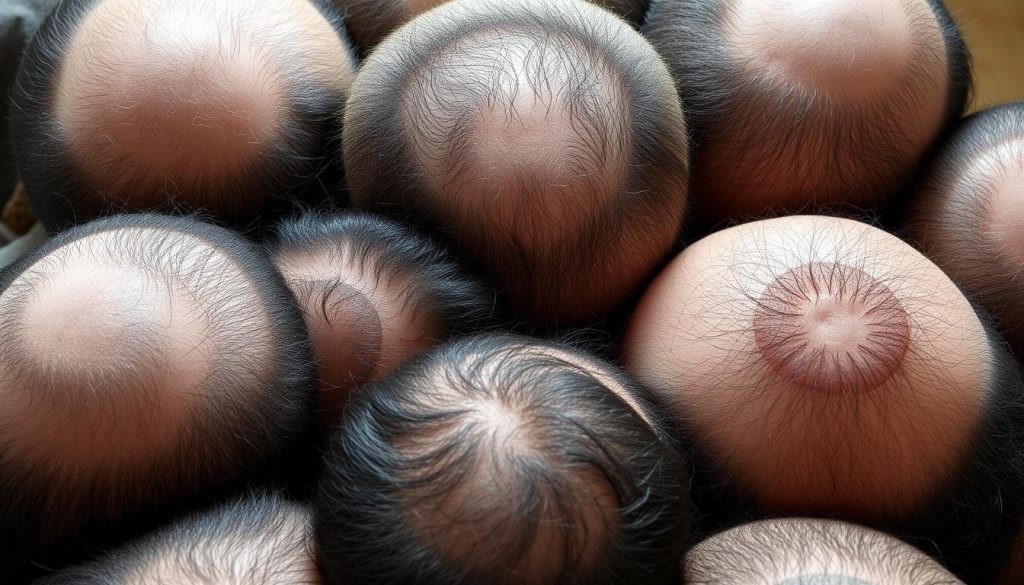
Alopecia is a condition that affects many people, making them question their appearance. Understanding alopecia is key to showing empathy to those facing hair loss today. This article aims to answer the big question: what causes alopecia hair loss? We’ll look into the causes of hair loss to understand this condition better.
We’re at a time when dermatology is advancing and awareness of alopecia is growing. Let’s dive into the different sides of this condition. We’ll learn more than just the basics. Join us as we explore alopecia and support those who face it every day.
Key Takeaways
- Gaining insight into alopecia’s role in contemporary hair loss
- Identifying the multilayered factors contributing to alopecia
- Understanding the personal and societal effects of hair loss
- Navigating the emotional aspect of alopecia with sensitivity
- Building a foundation of knowledge to support affected individuals
Alopecia Areata: An Overview
Alopecia areata is a big problem in the world of skin diseases, affecting millions. It’s an autoimmune disorder that causes sudden hair loss. This can really upset people who have it. It’s important for both patients and doctors to know a lot about this condition.
Defining Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is when your immune system attacks your hair follicles. This leads to hair loss, often in patchy bald spots on your scalp. Sometimes, it can get worse and cause more hair loss. For more details, check out this in-depth resource.
Identifying Different Types of Alopecia Areata
This condition comes in different forms. There’s Alopecia Totalis, where you lose all your scalp hair. And there’s Alopecia Universalis, where you lose hair all over your body. Knowing which type you have helps doctors figure out the best treatment.
Prevalence and Demographics
The number of people with alopecia areata varies. It affects different groups in different ways. Things like age, family history, and environment play big roles in who gets it and how it progresses.
| Age Group | Prevalence (%) |
|---|---|
| Children & Adolescents | 60 |
| Adults | 30 |
| Seniors | 10 |
Sharing stories of living with alopecia areata helps a lot. It shows the emotional and mental struggles people face. These stories help everyone understand and support those with alopecia better.
The Role of Autoimmune Disorders in Hair Loss
Understanding the link between autoimmune disorders and hair loss is key to finding treatments. These disorders can harm hair follicle health, causing hair loss. This is a big problem and shows there might be other health issues.
Autoimmunity: How it Affects Hair Follicles
Autoimmune disorders make the immune system attack the body’s own tissues. This can mess up hair growth, leading to hair loss. It’s not just a hair problem but a sign of deeper health issues.
Common Autoimmune Disorders Leading to Hair Loss
Some autoimmune disorders really affect hair follicles. Lupus can cause hair to thin or fall out in patches. Alopecia areata specifically attacks hair follicles, leading to unpredictable hair loss. Thyroid problems can also make hair thin all over.
Managing Autoimmune Related Hair Loss
Dealing with autoimmune hair loss involves medical and natural steps. This can include treatments for the immune system or ways to reduce stress. It’s all about finding what works best for each person’s health and life.
| Condition | Impact on Hair | Treatment Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Lupus | Thinning, patchiness | Medication, lifestyle changes |
| Alopecia Areata | Sudden bald patches | Steroid injections, topical treatments |
| Thyroid Disorders | Diffuse thinning | Thyroid medication, holistic health practices |
What Causes Alopecia Hair Loss
Understanding the causes of alopecia is key to finding the right treatments. This part looks at what leads to hair loss. Knowing the causes helps find the right help and support.
Hormonal Changes are a big factor in alopecia. Hormonal shifts can make hair follicles shrink, stopping normal hair growth. Things like thyroid issues, pregnancy, and menopause often cause these changes.
Genetic Predispositions also play a big role in hair loss. Genes can make hair follicles more sensitive to hormones, especially in androgenetic alopecia. For more info, check out this guide on hair loss causes.
Environmental Factors are another major alopecia trigger. Pollutants and toxins can weaken hair and scalp, causing more hair loss.
Each cause of alopecia needs a special treatment plan. This shows how important it is to know all the different triggers.
- Medications and medical treatments such as chemotherapy
- Extreme stress and sudden diet changes
- Harsh hair care practices leading to traction alopecia
Dealing with hair loss causes needs a wide approach. Changes in lifestyle, medical treatments, and sometimes counseling are all important for managing alopecia well.
| Cause Type | Common Triggers | Possible Interventions |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal | Menopause, Thyroid Issues | Hormone Replacement, Medical Therapy |
| Genetic | Family History of Baldness | Topical Treatments, Genetic Counseling |
| Environmental | Pollutants, Harsh Chemicals | Scalp Protection, Detoxification |
Androgenetic Alopecia and Genetic Influences
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as genetic hair loss, shows up as male and female pattern baldness. It’s the most common type of hair loss and is linked to genetics. It affects many people worldwide.
Understanding Male and Female Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness is seen as a receding hairline and thinning on top. Female pattern baldness keeps the hairline but thins on the top. Both are caused by hormones and how sensitive you are to them.
Genetic Factors and Their Implications for Treatment
Genetics play a big role in androgenetic alopecia. Knowing your family history can help predict your risk. New genetic tests help tailor treatments to fight hair loss.
Interventions and Preventative Measures
Today, we have many treatments for androgenetic alopecia, from creams to surgery. Early detection and understanding your genetic risk are key to preventing it.
| Treatment Type | Effectiveness | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Medicated Shampoos | Moderate | Mild Cases |
| Topical Minoxidil | High | Early to Moderate Stages |
| Hair Transplant Surgery | Very High | Advanced Hair Loss |
| Laser Therapy | Variable | Various Stages |
Examining the Impact of Stress on Hair Health
Stress and hair loss are closely linked, causing significant distress. Chronic stress can harm hair health, leading to thinning and loss. This section explores the biological reasons behind this, aiming for a deeper understanding.
Stress leads to hormonal changes in the body, affecting hair growth. It increases adrenal hormones, impacting the scalp and hair follicles. This hormonal shift is a major factor in stress-related hair loss, like telogen effluvium, where hair falls out too soon.
Understanding how stress hormones like cortisol impede follicle health is crucial for mitigating stress and hair loss.
Stress management is key to keeping hair healthy. Relaxation exercises, counseling, and a balanced diet help reduce stress. These actions promote a healthier hair growth cycle.
- Meditation and mindfulness exercises
- Regular physical activity
- Adequate sleep and hydration
- Professional therapy and support groups
While stress reduction strategies may not show results right away, their long-term benefits are significant. Regular stress management can slow or reverse hair damage. It promotes both physical and emotional well-being.
Telogen Effluvium: Shedding Light on Stress Hair Loss
Understanding telogen effluvium is key for those dealing with stress or big changes. It leads to hair loss and emotional stress. Knowing what causes it and how to recover can help a lot.
Identifying Telogen Effluvium Triggers
Many things can start telogen effluvium, like big stress, surgery, serious illness, or big diet changes. Finding out what causes it is the first step to fighting hair loss.
Distinguishing Between Chronic and Acute Cases
It’s important to know if you have acute telogen effluvium, which usually gets better in six months, or chronic hair loss. Chronic cases need more help. Knowing the type of hair loss helps find the right treatment.
Navigating Recovery and Regrowth
Getting better from hair loss means dealing with stress and creating a good environment for hair to grow back. It takes time and effort, but it’s worth it.
| Condition | Duration | Typical Triggers | Recovery Approaches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Telogen Effluvium | Less than 6 months | High stress, illness, surgery | Stress management, balanced diet |
| Chronic Hair Loss | More than 6 months | Ongoing stress, hormonal imbalances | Medical treatment, lifestyle changes |

Thinning Hair and Bald Spots: Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to know the early signs of alopecia. This helps you tell if you’re just losing hair normally or if it’s a sign of a bigger problem. We’ll show you how to spot hair thinning and bald spots.
Recognizing Early Indicators of Alopecia
Thinning hair is often the first sign of alopecia. It might not be obvious at first, so spotting it early is key. Bald spots can pop up suddenly and can be different sizes. They’re usually smooth and round, and they show up on the scalp.
Assessing the Severity of Hair Loss
When you see thinning hair and bald spots, it’s time to check how bad they are. Look at how many bald spots you have and how big they are. Also, see how fast your hair is thinning.
Making the Connection Between Symptoms and Underlying Causes
It’s important to connect the symptoms of hair loss to their causes. Bald spots and thinning hair are signs of hair loss. But knowing if it’s due to genetics, hormones, or autoimmune issues helps you treat it right.
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Common Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Thinning Hair | Genetic Predispositions | Topical Minoxidil, Finasteride |
| Bald Spots | Autoimmune Conditions | Corticosteroid Injections |
| Overall Hair Thinning | Hormonal Imbalances | Hormone Replacement Therapy |
Hair Loss Treatments: Options and Efficacy
Looking into hair loss treatments is key for those with alopecia. It brings hope and healing. There are many treatments, each with its own success rate. This shows why finding the right treatment is so important.
For treating alopecia, doctors have made many effective hair loss solutions. These range from easy-to-get products to more serious surgeries. Each one is made for different types and levels of hair loss.
- Topical treatments like minoxidil work well for mild cases by helping hair grow back.
- Oral meds, like finasteride, help with hair loss caused by hormones.
- Surgeries, like hair transplants, are a lasting fix but cost more and take longer to recover from.
Changing your lifestyle and diet also helps with hair loss treatments. Eating right and managing stress keeps your scalp healthy. This can stop hair loss from getting worse.
| Treatment Type | Efficacy | Recommended for |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Treatments | High in early stages | Mild alopecia |
| Oral Medications | Moderate to high | Progressive hair loss |
| Surgical Methods | High | Advanced cases |
Research is also looking into new effective hair loss solutions. This includes things like advanced materials and gene therapy. These could change how we treat alopecia in the future.
In conclusion, knowing about the different hair loss treatments helps people make better choices. Using a mix of old and new treatments is often the best way to help hair grow back. This keeps a person’s self-image strong.
Patchy Hair Loss: Investigating the Causes
When hair starts to thin in patches, it’s a cosmetic worry and might signal health problems. This article explores the causes of patchy hair loss. It also looks at how it’s different from other scalp issues. Knowing the causes is crucial for finding the right treatments and managing expectations, especially for those dealing with health issues.
Differentiating Between Alopecia Areata and Other Scalp Conditions
It’s important to tell alopecia areata, which causes round hair loss patches, from other scalp problems. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease, while other conditions like fungal infections or psoriasis are caused by outside factors. They might also have other skin symptoms. Knowing the exact condition helps find the right treatment for patchy hair loss.
Lifestyle Factors and Nutritional Deficiencies
Looking into lifestyle and nutrition is key to understanding patchy hair loss. Eating right is essential for healthy hair. Lack of vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and vitamins D and B can weaken hair. Changing your diet can help with hair loss, showing how our overall health affects our hair.
Connecting Skin Conditions to Hair Loss Patterns
Finally, skin conditions that affect hair growth and retention are important to consider. Some skin disorders can cause permanent hair loss by damaging the hair follicle. Early treatment can help prevent or lessen hair loss. On the other hand, some conditions might be treatable, allowing for hair loss management. It’s vital to understand these differences to choose the best treatment path.
FAQ
Q: What are the primary causes of alopecia hair loss?
A: Alopecia hair loss can come from many sources. Autoimmune disorders attack hair follicles by mistake. Genetic traits, like in androgenetic alopecia, also play a role. Hormonal shifts, environmental factors, and stress can also cause hair loss.
Q: What is alopecia areata and how is it different from other types of hair loss?
A: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that causes patchy hair loss. It’s different because it happens suddenly and can lead to total hair loss. This is not like gradual hair loss seen in aging.
Q: How do autoimmune disorders lead to hair loss?
A: Autoimmune disorders make the body attack healthy cells. When it targets hair follicles, it disrupts hair growth. This leads to hair loss. Managing the disorder can help control hair loss.
Q: Can stress cause hair loss, and if so, how?
A: Yes, stress can cause hair loss through telogen effluvium. It pushes hair follicles into a resting phase. This prevents new hair growth and causes existing hair to fall out.
Q: What is androgenetic alopecia and how is it influenced by genetics?
A: Androgenetic alopecia, or male/female pattern baldness, is hereditary. It’s influenced by genes that affect how hair follicles react to androgens. These hormones shorten the hair growth cycle and shrink follicles, causing thinning.
Q: What signs indicate the onset of alopecia?
A: Signs of alopecia include thinning hair, widening parts, and bald spots. Sudden shedding or finding a lot of hair in drains or brushes is also a sign. Catching these early can help with treatment.
Q: How can I assess the severity of my hair loss?
A: To assess hair loss, look at the pattern, amount shed, and duration. Medical professionals use scales like the Norwood and Ludwig scales to classify severity.
Q: Are there effective treatments available for those dealing with alopecia hair loss?
A: Yes, many treatments can help manage alopecia hair loss. Options include topical treatments, laser therapy, and hair transplant surgery. A dermatologist can help find the best treatment.
Q: What lifestyle factors can contribute to patchy hair loss?
A: Poor nutrition, extreme diets, high stress, and harsh hair care can cause patchy hair loss. Improving diet, managing stress, and gentle hair care can help.
Q: Can skin conditions on the scalp lead to hair loss?
A: Yes, scalp conditions like psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis can cause hair loss. Treating these conditions is key to preventing further damage and reversing hair loss.