Understanding clinical features of diabetes mellitus starts with seeing it as more than high sugar levels. It’s a complex metabolic disorder with big effects. Knowing the manifestations of diabetes mellitus is key for early diagnosis and treatment. This is important for millions worldwide.
By learning about diabetes mellitus, we can spot symptoms, understand their meaning, and use this in real healthcare. Each type of diabetes, like Type 1 and Type 2, has its own challenges. This article aims to explain these differences and help us understand diabetes mellitus better.
Let’s dive into diabetes mellitus and its many sides. We’ll have a detailed talk that could change lives for those at risk or already dealing with it.
Understanding Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition where the body can’t process glucose right. This leads to high blood sugar levels. Knowing how diabetes works is important for understanding its impact on health.
The signs of diabetes can vary but often include being very thirsty, needing to pee a lot, and losing weight without trying. High blood sugar levels can cause serious problems if not treated early.
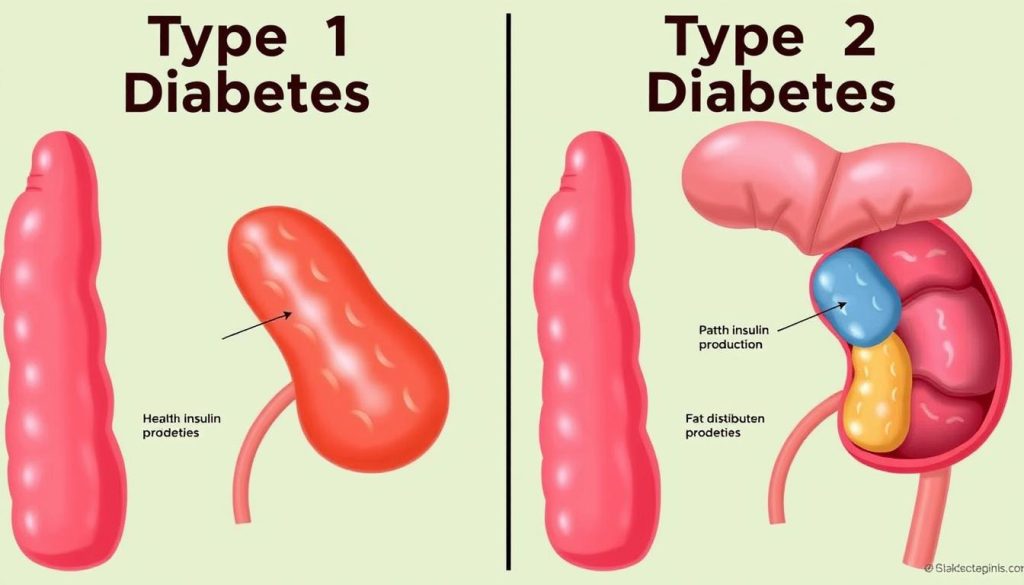
- Type 1 diabetes happens when the body attacks and destroys the cells that make insulin, leading to a lack of insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes is when the body’s cells don’t respond to insulin well, and eventually, the body makes less insulin.
Knowing the type of diabetes helps doctors find the best treatment. This is why learning about diabetes is so important. It helps make treatments more effective.
Diabetes affects people differently, depending on their genes, environment, and lifestyle. This shows the need for health plans that fit different groups. It’s key to fighting diabetes worldwide.
Learning about diabetes helps both patients and doctors. It leads to better ways to manage diabetes. This improves life for those with the condition.
Identifying Diabetes Signs and Symptoms
Knowing the early warning signs of diabetes is key for quick diagnosis and good management. Diabetes signs and symptoms can differ but often show a few main signs that should not be ignored.
Recognizing diabetes early can greatly improve patient outcomes and treatment plans. It’s vital to listen to your body and watch for any unusual changes that might be linked to diabetes:
- Frequent urination: Needing to urinate more often, often at night.
- Increased thirst: Feeling a strong need for liquids that doesn’t go away with drinking.
- Unexplained weight loss: Losing weight without changing diet or exercise.
- Extreme hunger: Feeling very hungry soon after eating.
- Visual disturbances: Blurry vision or other vision problems without a clear cause.
- Fatigue: Feeling very tired or weak without a clear reason.
- Slow healing wounds: Cuts or bruises that don’t heal quickly.
- Tingling or numbness: Feeling tingling or numbness in hands or feet, which could be nerve damage from high blood sugar.
If you see any of these diabetes signs and symptoms, see a healthcare professional for testing and confirmation. Ignoring these signs can lead to serious complications. So, it’s important to recognize diabetes as early as you can.
Type 1 Diabetes Characteristics
Understanding Type 1 diabetes characteristics means knowing it’s an autoimmune disease. It happens when the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-making cells in the pancreas. This attack is a key autoimmune diabetes feature. It makes the body need insulin from outside, making it insulin-dependent diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes often starts in kids and young adults but can happen at any age. It comes on quickly, unlike Type 2 diabetes, which develops slowly. People with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin right away, showing how urgent it is.
- Rapid onset of symptoms like frequent urination, extreme thirst, and unexplained weight loss.
- Constant management required through daily insulin injections or a pump.
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels to prevent complications.
In summary, the unique Type 1 diabetes characteristics and autoimmune diabetes features need a deep understanding and active management. It’s not just a chronic disease; it’s a lifelong commitment to careful monitoring and lifestyle changes.
Type 2 Diabetes Manifestations
It’s important to know the signs of Type 2 diabetes, also called adult-onset diabetes. This type of diabetes usually starts in adults. It’s linked to insulin resistance symptoms, being overweight, and not being active enough.
The main signs of Type 2 diabetes are high blood sugar, needing to pee a lot, feeling very thirsty, and losing weight without trying. These symptoms happen because the body can’t use insulin well. Spotting these signs early can lead to getting help from a doctor sooner.
- Increased fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
| Manifestation | Common in Type 1 | Common in Type 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Early onset | Yes | No |
| Insulin resistance | No | Yes |
| Associated with obesity | No | Yes |
| Genetic predisposition | Less significant | More significant |
Knowing the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is key. Both can harm your health if not treated. But, how you manage them is different. This is because of how well the body uses insulin and reacts to it.
Atypical Diabetes Presentations
Diabetes comes in many forms, not just type 1 and type 2. Conditions like LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults) and MODY (Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young) are different. They show unusual diabetes symptoms that can confuse doctors and delay treatment.
MODY and LADA have their own signs. MODY starts in teens or early twenties and looks like type 1 diabetes but isn’t. LADA starts in adults and looks like type 2 but quickly needs insulin because of an autoimmune attack.
- Unusual Diabetes Symptoms: Includes conditions like hyperglycemia that occur at atypical ages or weight categories.
- LADA: Often misclassified, this condition features slow-onset type 1 diabetes in adults and requires ongoing monitoring of autoantibodies.
- MODY: Often involves several gene mutations, with different subtypes affecting how the body manages glucose.
| Type | Presentation | Common Misdiagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| MODY | Mild to moderate steady hyperglycemia | Type 1 Diabetes |
| LADA | Adult onset with slow progression | Type 2 Diabetes |
Understanding MODY and LADA is key for better treatment. Doctors should look for these conditions in patients with unusual symptoms. This can lead to better care and outcomes for patients.
Standard Diagnostic Criteria for Diabetes
Getting a correct diabetes diagnosis depends on specific tests. The A1C test, fasting glucose levels, and oral glucose tolerance tests are key. Each test plays a vital role in diagnosing diabetes, helping doctors manage the condition well.
The A1C test is essential for diabetes diagnosis. It shows average blood sugar levels over 2 to 3 months. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher on two tests means diabetes.
Fasting glucose levels are also important. A reading of 126 mg/dL or higher after fasting confirms diabetes. Oral glucose tolerance tests measure blood sugar two hours after a glucose drink. A result of 200 mg/dL or higher also confirms diabetes.
| Test Type | Diagnostic Benchmark | Condition Indicated |
|---|---|---|
| A1C Test | 6.5% or higher | Diabetes |
| Fasting Glucose Levels | 126 mg/dL or higher | Diabetes |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | 200 mg/dL or higher | Diabetes |
Knowing the diagnostic criteria for diabetes is key for early detection and management. Accurate diagnosis through these tests helps manage the disease. It also prevents complications from undiagnosed diabetes.
Diabetes Mellitus Clinical Features
It’s key to know the diabetes mellitus clinical features for early detection and treatment. These include hyperglycemia symptoms and diabetes physical signs. These signs show the body can’t handle blood sugar levels right.
Hyperglycemia symptoms show up when blood sugar stays high. You might feel really thirsty (polydipsia), need to pee a lot (polyuria), and lose weight without trying. These signs are important and mean you should see a doctor right away.
- Increased thirst and dry mouth
- Frequent urination, even at night
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Looking at diabetes physical signs helps us understand diabetes better. For example, acanthosis nigricans—a darkening and thickening of skin folds, mainly around the neck and armpits—points to insulin resistance. This is common in Type 2 diabetes.
| Physical Sign | Description | Commonly Associated Type |
|---|---|---|
| Acanthosis nigricans | Dark, thickened patches of skin | Type 2 |
| Diabetic dermopathy | Brown, scaly patches on the skin | Type 1 and Type 2 |
It’s important to watch for both hyperglycemia symptoms and diabetes physical signs during health checks. Spotting these diabetes mellitus clinical features early can help manage diabetes better. This can lead to better health outcomes for people with diabetes.
Distinguishing Diabetes Types
It’s key to know the different types of diabetes in the medical world. Doctors use a mix of patient history, tests, and understanding of diabetes types to figure this out. They look at genetic markers to tell diabetes types apart.
Assessment of Early Onset Diabetes
Diabetes that starts early, or juvenile diabetes, is hard to diagnose and manage. Doctors must pay close attention to symptoms and how well the body uses insulin in young patients. This helps tell if it’s type 1 or type 2 diabetes, which can now show up in younger people.
Evaluation of Insulin Resistance and Beta Cell Dysfunction
Checking for insulin resistance and beta cell problems is key for type 2 diabetes. Doctors run tests to see how well the body uses insulin and how the insulin-making cells in the pancreas are doing.
Correlation with Genetic Markers
Knowing if you might get diabetes because of your genes is important. Genetic markers help doctors see if you might be at risk. This helps them plan better ways to prevent diabetes.
Metabolic Syndrome in Diabetes
Metabolic syndrome in diabetes, also known as insulin resistance syndrome, is a group of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease. These include high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess belly fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels. It’s important to understand how these conditions affect diabetes to manage and prevent them effectively.
Criteria for Metabolic Syndrome Diagnosis
The criteria for metabolic syndrome are key for diagnosing it. To diagnose, you need to have at least three of the following: belly fat, high fasting glucose, high triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, and high blood pressure. These factors can worsen the metabolic risks in diabetes patients.
Implications of Metabolic Syndrome in Diabetes Management
Managing diabetes with metabolic syndrome is challenging. The presence of multiple risk factors makes standard treatments less effective. It requires a detailed approach that includes lifestyle changes and medical interventions. This highlights the need for a team effort to manage blood sugar and metabolic disorders.
Preventing Metabolic Syndrome in Diabetic Patients
Preventing metabolic syndrome in diabetic patients relies on lifestyle changes. Regular exercise, healthy diet, and sometimes medication are key. Focusing on losing weight, staying active, and eating well can greatly reduce these risks.
| Condition | Impact | Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| High Blood Pressure | Increases cardiovascular risk | Diet, medication, regular monitoring |
| High Blood Sugar | Heightens risk of organ damage | Blood sugar monitoring, anti-diabetic medications |
| Abdominal Obesity | Aggravates metabolic imbalance | Weight management, physical activity |
| Abnormal Lipids | Escalates risk of arteriosclerosis | Dietary changes, statins |
Understanding Diabetes Complications and Symptoms
Diabetes is more than just blood sugar levels. It affects almost every part of the body. It’s important for patients and caregivers to know about diabetes complications and symptoms. This knowledge helps manage the disease and avoid serious problems.
As diabetes gets worse, the risk of nerve damage, kidney problems, and heart disease goes up. This shows why it’s key to watch your health closely and act fast. We’ll look at some common diabetes problems and how they affect the body.
| Complication | Description | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Neuropathy | High blood sugar damages nerves, causing numbness, pain, and weakness in legs and feet. | Numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness in affected areas. |
| Nephropathy | Kidney damage from high blood sugar, leading to waste buildup and swelling. | Swelling in feet and ankles, higher protein levels in urine, nausea, fatigue. |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Heart and blood vessel problems from blood sugar changes, increasing heart attack and stroke risk. | Chest pain, shortness of breath, increased heart rate. |
Knowing about diabetes complications and symptoms helps catch problems early. This can slow down the disease’s progress. Learning about these issues is key to a healthier life with diabetes.
For patients, knowing the signs of chronic diabetes effects can save lives. Regular doctor visits are vital for managing diabetes well. They help spot problems before they get worse.
Consequences of Long-Term Hyperglycemia
Long-term hyperglycemia can harm major organs and systems. It’s important for people with diabetes to understand these risks. This knowledge helps them take steps to protect their health.
Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Chronic hyperglycemia can severely affect heart health. It damages blood vessels and makes arteries less flexible. This can lead to heart problems like high blood pressure and heart attacks.
Impact on Kidney Health
Managing blood sugar is key to protecting kidneys. High blood sugar can damage kidney filters, leading to kidney failure. Regular kidney checks are vital for diabetic patients.
Diabetic Retinopathy and Vision Concerns
Diabetic retinopathy can cause vision loss. It happens when blood sugar levels damage the retina’s blood vessels. Regular eye exams can help catch problems early and prevent vision loss.
| Complication | Description | Preventative Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease | Includes heart diseases caused by damage to the blood vessels due to high glucose levels such as atherosclerosis and hypertension. | Regular exercise, medication adherence, balanced diet, and routine medical checks. |
| Diabetic Nephropathy | Kidney damage that occurs in people with diabetes, which could lead to kidney failure. | Control of blood sugar levels, blood pressure management, and early screening for kidney function. |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | Potentially blinding condition caused by prolonged high blood sugar impacting retina’s blood vessels. | Regular dilated eye exams, controlling diabetes, and managing overall health. |
Psychosocial Considerations in Diabetes
Living with diabetes is tough, both physically and mentally. It can lead to burnout, mental health issues, and a lower quality of life. It’s key to understand these challenges to manage diabetes well and improve life satisfaction.
Dealing with Diabetes Burnout
Diabetes burnout is a state of feeling emotionally and mentally drained. It happens when managing diabetes every day becomes too much. To fight it, set achievable goals, make time for mental health, and recognize the effort in managing stress.
Seeking help from mental health services for diabetes is also helpful. They offer professional advice and support.
Emotional and Mental Health Support
Diabetes can be emotionally heavy. But, having a strong support network can help. This includes family, friends, healthcare providers, and support groups.
These groups are great for sharing experiences and tips. They help improve mental health and emotional well-being. Also, getting professional mental health services can greatly improve psychological well-being.
Improving Quality of Life with Diabetes
Improving life with diabetes is more than just medical care. It’s about a holistic approach that includes psychological support and lifestyle changes. Learning to manage self-care fatigue and joining community activities can boost well-being.
Regular talks with healthcare professionals who focus on psychological care are also important. They help improve quality of life and ensure long-term health and emotional well-being.
Diabetes Management Techniques and Lifestyle Changes
Living with diabetes means using diabetes management techniques carefully. It’s about using medicine, eating right, and changing your lifestyle to control diabetes naturally. Doctors now have many treatments, like new insulin and pills, to help.
Checking your blood sugar often and getting A1C tests are key. Working with your doctor to make a plan that fits you is very important. This helps keep your blood sugar in check and improves your health.
Lifestyle changes for diabetes are very important. Starting with regular exercise is a good first step. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate activity most days to help your body use insulin better.
Eating well is also key. Choose foods high in fiber, lean proteins, and complex carbs. Avoid foods high in sugar and fat. Also, finding ways to reduce stress, like meditation, can help keep your blood sugar stable.
If you want to try controlling diabetes naturally, talk to your doctor about supplements like cinnamon or chromium. These natural helpers, along with getting enough sleep, are becoming more popular in diabetes care. But remember, they should be used with your doctor’s advice and not instead of your regular treatment.
By making smart choices and taking care of yourself, you can manage diabetes well. This can help prevent serious problems down the line.
FAQ
Q: What are the clinical features of diabetes mellitus?
A: Diabetes mellitus shows signs like increased thirst and urination. You might also lose weight without trying, feel tired, see blurry vision, and have slow-healing wounds.
Q: How does diabetes mellitus affect the body?
A: Diabetes messes with how your body uses insulin. This leads to high blood sugar levels. Over time, it can harm many parts of your body.
Q: What are the early warning signs of diabetes that should not be ignored?
A: Watch out for signs like needing to pee a lot, feeling very thirsty, and hungry all the time. You might also lose weight, feel tired, see blurry vision, and have numbness in your hands or feet.
Q: What distinguishes Type 1 diabetes from Type 2?
A: Type 1 diabetes happens when your body attacks the insulin-making cells in your pancreas. This means you can’t make enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes is when your body doesn’t use insulin well and makes less over time.
Q: What are the typical signs of Type 2 diabetes?
A: Signs of Type 2 diabetes include feeling very hungry and thirsty, needing to pee a lot, and changes in weight. You might also feel tired, see blurry vision, get sick often, and have dark skin patches, usually in the neck and armpits.
Q: Can diabetes present in atypical ways?
A: Yes, diabetes can show up differently, like in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA) or Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY). These types don’t always look like the usual Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes.
Q: What are the standard diagnostic criteria for diabetes?
A: Doctors use tests like the A1C test, fasting blood glucose, or an oral glucose tolerance test to diagnose diabetes. A level of 6.5% or higher on the A1C test, 126 mg/dL or higher fasting, or 200 mg/dL or higher on the glucose test means you have diabetes.
Q: What physical signs may indicate diabetes mellitus?
A: Signs of diabetes include dark skin patches (acanthosis nigricans), signs of insulin resistance, being overweight, slow-healing sores, dry skin, and signs of nerve damage.
Q: How are different types of diabetes distinguished?
A: Doctors look at your age when symptoms start, your weight, if you have certain antibodies, how fast symptoms come on, your family history, and how you respond to treatments to figure out the type of diabetes you have.
Q: What constitutes metabolic syndrome in the context of diabetes?
A: Metabolic syndrome is a group of conditions like high blood pressure, high blood sugar, being overweight around the waist, and bad cholesterol levels. It raises your risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
Q: How can metabolic syndrome be prevented in diabetic patients?
A: To prevent metabolic syndrome, diabetics should eat healthy, exercise regularly, keep a healthy weight, and might need medication to control risk factors.
Q: What are the complications and symptoms indicating the progression of diabetes?
A: Signs of diabetes getting worse include heart problems, kidney damage, nerve damage, vision issues, skin problems, hearing loss, and being more prone to infections.
Q: What are the long-term effects of hyperglycemia on the cardiovascular system?
A: Long-term high blood sugar can cause heart disease, heart attacks, strokes, atherosclerosis, and hypertensive heart disease.
Q: How does diabetes impact kidney health?
A: Diabetes can damage your kidneys by affecting the blood vessels. This can lead to kidney failure or the need for dialysis or a transplant.
Q: Why is regular eye examination important for diabetics?
A: Diabetics need regular eye exams to catch early signs of diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Early treatment can prevent serious vision loss.
Q: What is diabetes burnout and how is it managed?
A: Diabetes burnout is feeling frustrated and exhausted from managing diabetes. It can lead to neglecting self-care. To manage it, get emotional support, adjust your treatment plan, and consider talking to a mental health professional.
Q: What lifestyle changes are recommended for effectively managing diabetes?
A: To manage diabetes, eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, quit smoking, drink alcohol in moderation, and check your blood sugar levels often.