Understanding alopecia goes beyond just looking at the surface. It’s about knowing the causes of alopecia and the many alopecia risk factors. This article aims to make hair loss easier to understand. It helps readers spot signs of alopecia early.
At the heart of this is alopecia diagnosis. It shows what causes hair loss for each person. As we explore “How do you get alopecia?” we find that the answers are complex, just like the condition itself.
Starting to understand alopecia means looking at how the body can lose hair. This is a confusing and upsetting issue for many. We look at genetics, autoimmune diseases, environmental factors, and stress to help those with alopecia.
Key Takeaways
- Knowing about alopecia risk factors helps catch it early and manage it better.
- Genetics play a big part in who might get alopecia.
- Autoimmune diseases, environmental factors, and hormonal imbalances are key in diagnosing alopecia.
- How you feel emotionally and what you eat can make alopecia better or worse.
- Knowing what causes alopecia helps both people and doctors make better treatment plans.
Understanding Alopecia: An Overview
Alopecia is a condition that causes hair loss. It comes in different forms and affects many people around the world. To prevent, manage, and treat alopecia, we need to understand its types and symptoms. We also need to know how it affects people emotionally.
Alopecia is divided into types like alopecia areata, androgenetic alopecia, and telogen effluvium. Each type has its own challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms can range from small bald spots to complete hair loss, affecting the scalp and sometimes other parts of the body.
- Alopecia Areata: Often results in sudden, patchy hair loss.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Commonly referred to as male or female pattern baldness, it involves a thinning crown and receding hairlines.
- Telogen Effluvium: Typically temporary, this condition sees hair thinning over the scalp and is often triggered by physical or psychological stress.
Alopecia affects more than just how we look. It can hurt our self-esteem and mental health. That’s why managing alopecia is important for both our skin and our minds.
When it comes to treatment, there are many options. These include topical treatments, oral medications, and even advanced therapies like corticosteroid injections and ultraviolet light therapy. The right treatment depends on the type and severity of alopecia, as well as the patient’s needs and medical history.
Preventing alopecia involves reducing risk factors and keeping hair healthy. This includes eating right, managing stress, and seeing a doctor regularly. It’s important for those at risk or showing symptoms to get help early.
In summary, understanding alopecia means knowing its different forms, its impact on our lives, and the many ways to manage and treat it. This knowledge is the first step in exploring this complex condition further.
Genetic Factors in Alopecia
Looking into the genetic roots of alopecia helps us understand hair loss better. It shows how inherited traits can affect hair loss. This knowledge helps us see what we might get from our ancestors.
Alopecia Genetics: Tracing Your Family History
Looking into your family’s history of alopecia can give you clues. It’s not just about losing hair. It’s about understanding the mix of genes from both parents. So, it’s key to check both sides of your family for hair loss signs.
Genetic Predisposition: Are You at Risk?
Knowing if you’re at risk for alopecia can help you take care of your hair. It’s about finding markers that show you might get alopecia. This can be through genetic tests or family history.
Genetics play a big role in alopecia, but they don’t mean you’ll definitely lose your hair. Lifestyle and environment also matter. But, if you’re predisposed, watch for symptoms and take good care of your scalp and hair.
Autoimmune Causes of Alopecia
Understanding autoimmune alopecia means knowing how the immune system affects hair follicles. Normally, the immune system fights off harmful invaders. But in autoimmune alopecia, it attacks healthy hair follicles, causing hair loss. This shows how complex autoimmune disorders can be, as the body fights itself.
Alopecia diagnosis for autoimmune cases involves several steps. Doctors look at the hair loss pattern, do scalp biopsies, and run blood tests. This helps figure out the autoimmune cause of alopecia. Knowing this can help choose the right treatment, which often aims to calm down the immune system.
“Recognizing the signs early and accurately diagnosing autoimmune alopecia can significantly increase the effectiveness of treatment strategies.”
- Initial Clinical Assessment
- Scalp Biopsy
- Blood Tests
It’s key for doctors to tailor treatments based on each person’s diagnosis. This is why managing autoimmune alopecia needs a careful approach. Treatments might include immunosuppressive drugs or corticosteroids. These can help reduce the immune system’s overactivity.
| Treatment | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Immunosuppressive Drugs | Drugs that help suppress the immune system to prevent it from attacking hair follicles. | Varies by individual |
| Corticosteroids | These are anti-inflammatory drugs that can be taken orally, injected, or applied topically. | Can be effective with prolonged use |
| Topical Immunotherapy | A chemical solution applied directly to the scalp to alter the immune response. | Effective in some cases |
Environmental Triggers for Alopecia
Our surroundings play a big role in our hair health. Environmental triggers and chemical exposures can cause hair loss. Knowing about these can help us make better choices for our hair.
Chemical Exposures And Hair Loss
We are surrounded by chemicals every day. From air pollution to cleaning products, they can harm our hair. Some chemicals in hair dyes and treatments can weaken hair follicles. It’s important to be aware of these chemicals to protect our hair.
- Avoid harsh chemical treatments and choose natural hair care.
- Clean your scalp regularly to remove chemicals.
- See a dermatologist for hair products that suit you.
Climatic Influences on Hair Health
The weather also affects our hair. Too much sun or cold winds can make hair brittle and fall out. Changing our hair care routine with the seasons can help protect our hair.
- Wear hats or scarves to protect from UV rays and wind.
- Use the right hair products for each season.
- Get advice on the best hair care for each season.
In summary, chemicals and weather are big factors in hair loss. Being aware and making the right changes can help prevent and manage hair loss.
Hormonal Imbalances and Alopecia
It’s important to understand how hormonal imbalances and hair loss are connected. Hormonal changes happen at different times in life, like during pregnancy and menopause. These changes can greatly affect hair health.
Hormones like androgens, insulin, and cortisol affect hair growth. When these hormones are out of balance, it can cause hair loss or thinning. For more information on how hormones impact hair, check out this study here.
Big life changes, like having a baby or going through menopause, can change hormone levels. This can lead to noticeable changes in hair texture and volume. Here’s a quick look at how hormonal imbalances are linked to different types of alopecia:
| Type of Hormonal Imbalance | Associated Hair Loss Condition |
|---|---|
| Increased Androgens | Androgenetic Alopecia |
| Thyroid Dysfunctions | Anagen Effluvium |
| Low Estrogen Levels | Telogen Effluvium during Postpartum Period |
| High Cortisol Levels | Stress-Related Alopecia |
Fixing hormonal imbalances often needs a mix of medical help and lifestyle changes. To keep hair healthy during hormonal changes, eat well, manage stress, and sometimes use hormone therapies. Knowing about hormonal hair loss early and getting treatment can make a big difference.
Emotional and Psychological Stress as a Factor
The effects of emotional stress and psychological stress on our bodies are well-known. They can cause stress-related hair loss. Learning more about this link helps us find ways to prevent and treat it.
Stress-Related Hair Loss: Understanding the Connection
Stress-related hair loss, or alopecia areata, is linked to stress. A study found that stress hormones can start hair loss. This shows how stress and hair health are connected.
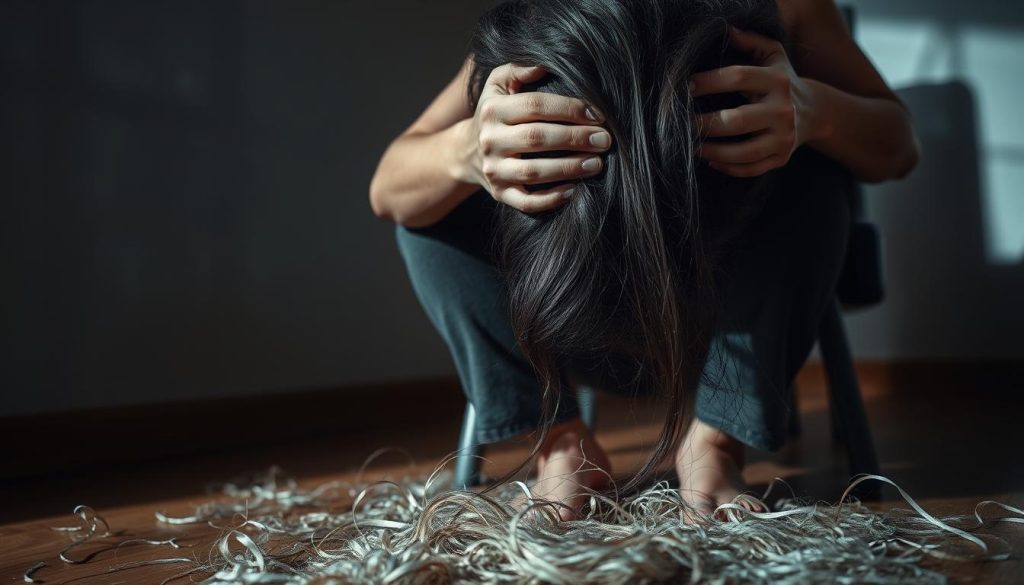

Managing Stress to Prevent Alopecia
Reducing emotional and psychological stress is key to preventing hair loss. Mindfulness, exercise, and therapy can help. By using these methods, we can lower the chance of stress-induced alopecia.
By handling emotional stress, we can keep our mental and hair health in check. This is a complete way to take care of ourselves.
Dietary Impacts on Hair Health
Looking into how our diet affects hair health shows us a lot. It tells us how what we eat can help or hurt our hair. Eating the right foods is key to keeping our hair healthy and preventing hair loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Hair Loss
Not getting enough nutrients can lead to hair loss. Lack of iron, zinc, vitamins D, B12, and A can stop hair growth. This makes hair follicles rest too early, causing hair to fall out.
Eating a balanced diet can help prevent this hair loss. Foods rich in these nutrients are important for hair health.
The Role of Diet in Managing Alopecia
Diet plays a big role in preventing alopecia. Eating foods full of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants strengthens hair follicles. This makes hair more resistant to loss.
Adding more protein and omega-3 fatty acids to your diet helps too. Foods like salmon and flaxseeds are great for this.
In short, what we eat greatly affects our hair. Fixing nutritional gaps through diet is a good way to manage and prevent alopecia. If you’re losing hair, changing your diet might be a smart move for better hair care.
Medical Conditions With Alopecia as a Symptom
It’s important to know how different health issues can cause alopecia. This knowledge helps doctors diagnose and treat these conditions better. Many health problems can lead to hair loss, affecting how well a person feels and lives.
Alopecia is not just a hair loss issue. It can also be a sign of other health problems. Finding out what’s causing the hair loss is key to treating it right.
Thyroid problems, like hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, are linked to alopecia. These issues affect hormone levels, which are crucial for hair growth. Autoimmune diseases, like lupus, also cause hair loss because the immune system attacks healthy hair follicles.
- Anemia, caused by a lack of red blood cells, can lead to hair thinning and loss. This is because the body and hair follicles don’t get enough oxygen.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is known for hormonal imbalances. It often causes hair to thin.
- Scalp infections and other skin problems can also cause hair loss. This shows why checking the scalp is so important.
Understanding these medical conditions is crucial. It shows why a full health check is needed when someone loses hair without a clear reason.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into the causes of alopecia and how to manage it. It’s a complex issue, influenced by genetics, environment, hormones, and stress. Understanding these factors is key to managing alopecia.
There are many treatment options for alopecia, each suited to different needs. Getting help from healthcare experts is crucial. They can create a treatment plan that works for you.
Managing alopecia is not just about treatments. It also involves changing your lifestyle, eating better, and managing stress. This holistic approach helps you stay strong and hopeful. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
FAQ
Q: What are the primary causes of alopecia?
A: Alopecia can come from many sources. Genetics, autoimmune diseases, and hormonal imbalances are common causes. Environmental triggers, stress, and certain medical conditions also play a role.
Q: Can you elaborate on the risk factors associated with alopecia?
A: Yes, several factors increase your risk of alopecia. Family history, autoimmune diseases, and stress are key. Environmental chemicals, extreme weather, and hormonal changes also matter.
Q: How is alopecia diagnosed?
A: Doctors diagnose alopecia by examining your hair and scalp. They also look at your medical history. Sometimes, they use tests or a scalp biopsy to find the cause.
Q: Are there ways to prevent alopecia?
A: While some alopecia types can’t be prevented, you can lower your risk. Eat well, manage stress, and avoid harsh hair treatments. Taking care of your health can help.
Q: What role do genetics play in the development of alopecia?
A: Genetics are a big factor in alopecia, especially in androgenetic alopecia. If your family has a history of hair loss, you’re more likely to get it.
Q: How do autoimmune disorders contribute to alopecia?
A: Autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata cause hair loss. The immune system attacks hair follicles. This is a main reason for alopecia in these cases.
Q: How do environmental factors trigger alopecia?
A: Chemicals in hair dyes or treatments and extreme weather can harm hair follicles. This can lead to alopecia.
Q: What hormonal imbalances are associated with hair loss?
A: Hormonal issues, like androgen or thyroid problems, can cause hair loss. Changes during pregnancy or menopause also affect hair.
Q: Can emotional and psychological stress cause hair loss?
A: Yes, stress can cause temporary hair loss, known as telogen effluvium. Long-term stress can make other alopecia types worse.
Q: How does diet affect the health of my hair?
A: A balanced diet with proteins, vitamins, and minerals is key for hair health. Lack of these nutrients can weaken hair and lead to loss.
Q: Which medical conditions can manifest alopecia as a symptom?
A: Alopecia can be a sign of conditions like thyroid disorders, anemia, lupus, and PCOS. These conditions affect hair growth.
Q: What are some treatment options for managing alopecia?
A: Treatments depend on the type and cause of hair loss. Options include topical medications, injections, oral treatments, light therapy, or surgery. Lifestyle changes and support are also important.
Q: Are there specific lifestyle changes that help manage alopecia?
A: Yes, managing alopecia involves reducing stress, avoiding tight hairstyles, and using gentle hair care. Protecting hair from damage and eating well are also important.