Exploring what is alopecia disease takes us into a common issue affecting many people—hair loss. It’s not just about being bald. Alopecia is a complex condition with different types. We start by understanding alopecia symptoms, the various forms of hair loss, and the treatments available.
This introduction sets the stage for a deeper look. We’ll see how alopecia affects people’s lives, both physically and emotionally.
Key Takeaways
- Alopecia is more than mere baldness; it’s a diverse range of hair loss conditions.
- Recognizing the early signs can lead to a deeper understanding of the types and severity of the disease.
- There are multiple alopecia symptoms that warrant attention beyond the visibly thinning hair.
- Insight into alopecia treatment can offer hope and direction for those affected.
- Our approach is empathetic and enlightening, aiming to support and educate about alopecia disease.
Understanding Alopecia Disease
Alopecia is more than just hair loss. It’s a range of conditions that affect people of all ages and backgrounds. This section will help you understand what alopecia disease is, its different types, and how common it is.
The Basic Definition of Alopecia
Alopecia means losing hair from anywhere on the body. There are many types, from small patches to complete hair loss. Unlike normal hair fall, alopecia shows up as clear bald spots or thinning. Knowing these signs is key to catching alopecia early.
How Common is Alopecia?
Alopecia affects millions of people worldwide. It’s not just about looks; it’s a serious health issue. It can cause a lot of emotional and psychological pain.
| Type of Alopecia | Description | Common Age Group |
|---|---|---|
| Alopecia Areata | Sudden, patchy hair loss | Mostly young adults and children |
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Gradual thinning of hair, commonly known as male or female pattern baldness | Adults, increasingly prevalent with age |
| Telogen Effluvium | Temporary hair loss typically triggered by stress or a traumatic event | Any age, more common in women |
| Anagen Effluvium | Rapid hair loss resulting from medical treatment, like chemotherapy | All ages, depending on treatment necessity |
Knowing about the different types of alopecia helps those affected get help early. Learning about alopecia disease is important for managing its physical and emotional effects.
Exploring the Different Alopecia Types
Understanding alopecia means learning about its main types: alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis. Each type shows how this autoimmune disorder affects people differently.
- Alopecia areata: It causes patchy hair loss, often in small, round patches that may overlap.
- Alopecia totalis: This type means losing all hair on the scalp, showing a more uniform loss than areata.
- Alopecia universalis: It’s the most severe, leading to hair loss all over the body, including the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair.
These alopecia types affect not just how people look but also their mental health. Knowing the differences is key for managing and treating the condition.
| Type | Description | Impact on Scalp | Impact on Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alopecia Areata | Small, patchy hair loss | Partial | None |
| Alopecia Totalis | Complete scalp hair loss | Total | None |
| Alopecia Universalis | Total hair loss on scalp and body | Total | Total |
The visual differences among alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis guide treatment methods. Each type needs specific treatments based on the extent and type of hair loss. This affects how people recover and the support they need.
Recognizing the Signs of Alopecia
Spotting the early signs of hair loss is key for those worried about alopecia. Knowing the first signs can lead to early action and better results. Hair loss can have many causes, but certain signs point to alopecia.
Early Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Early alopecia symptoms can be subtle. You might find more hair on your pillow or in the shower. These signs might seem like normal hair loss at first. But, they could signal the start of baldness.
Other symptoms to watch for include:
- Noticeable thinning of hair on the top of your head
- Small, round patches of hair loss in particular areas
- Sudden loosening of hair, leading to substantial hair fall during combing or washing
Visual Indicators of Progressive Hair Loss
As alopecia gets worse, changes become more obvious and concerning. Hair thinning gets worse, and patches of bald scalp appear. Look out for these signs to know when to see a doctor:
| Early Stage | Progressive Stage |
|---|---|
| Widening parts | Larger bald spots |
| Reduced hair volume | Complete baldness in areas |
| Thinning at the temples | Visible scalp in daylight |
Spotting these signs is the first step to managing alopecia. Early action is crucial for controlling baldness.
What Causes Alopecia? Unraveling the Triggers
Looking into alopecia causes shows a mix of genetic factors, autoimmune hair loss conditions, and outside influences. This part explains how these elements work together to cause different types of alopecia.
Genetics are a big part of who might get alopecia. If your family has a history of hair loss, you might be more likely to get it too. Also, autoimmune diseases can cause alopecia areata. In this case, the immune system attacks hair follicles, causing hair to fall out.
| Trigger | Impact on Hair Loss | Associated Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Increased Susceptibility | Pattern Baldness, Alopecia Areata |
| Autoimmune Dysfunction | Destruction of Hair Follicles | Alopecia Areata, Totalis |
| Environmental Influences | Aggravates Existing Conditions | Scarring Alopecia |
Stress, diet, and chemicals can also make alopecia worse. The complex nature of alopecia causes shows why we need a complete understanding of it. This is key to managing this condition effectively.
What Is Alopecia Disease: A Medical Overview
Alopecia disease is a mix of genetics and autoimmune reactions. It leads to different types of hair loss, like autoimmune hair loss. This part will explain the complex biology behind it and the role of genetics in alopecia.
Autoimmune Factors in Alopecia Areata
In alopecia areata, the immune system attacks healthy hair follicles. It sees them as threats. This can cause sudden hair loss, affecting both men and women of all ages. Knowing about these autoimmune factors is key to finding the right treatments.
Genetic Predisposition and Environmental Influences
Genetics also play a big part in alopecia areata. Research shows that family history can increase the risk. Stress, diet, and chemicals can also trigger or worsen the condition.
The mix of genetics and environment explains why people react differently to alopecia. Doctors can use this knowledge to predict how the condition will progress. They can also suggest ways to prevent it.
| Factor | Role in Alopecia Development | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Susceptibility | Predisposes individuals to hair loss | High (influences onset and severity) |
| Autoimmune Dysfunction | Leads to hair follicle attack | Variable (depends on immune system status) |
| Environmental Trigger | May activate underlying genetic predisposition | Moderate to High |
In conclusion, treating alopecia requires looking at both autoimmune and genetic factors. A personalized treatment plan is needed, based on a detailed medical check-up.
Diagnosing Alopecia: From Initial Consultation to Confirmation
Experiencing unexplained hair loss can be scary. It’s important to know who to turn to and what tests are done. This knowledge helps find the right treatment and brings peace of mind.
The Role of Dermatologists in Diagnosing Hair Loss
Dermatologists are experts in hair loss. They start with a dermatologist consultation. They look at your medical history, diet, and lifestyle to understand your hair health.
The consultation also includes a physical check of your hair and scalp. This helps them see the extent and pattern of your hair loss.
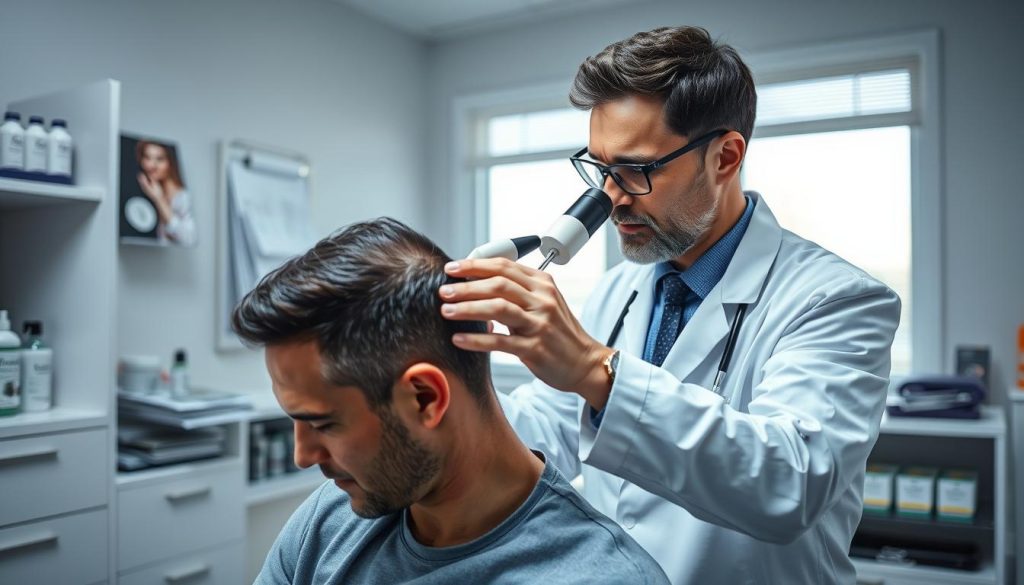
At places like NYU Langone, dermatologists use advanced tools for diagnosing hair loss. They use trichoscopy to see the scalp closely. This helps them figure out the type of alopecia you have, which is key for treatment.
What Tests Can Confirm Alopecia?
To confirm alopecia, several tests are done. These tests are called alopecia confirmation tests. They include scalp biopsies, blood tests, and pull tests.
Scalp biopsies check the scalp skin. Blood tests look for health issues like thyroid disease. Pull tests measure how much hair is lost.
| Test Type | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Scalp Biopsy | Small section of scalp skin taken | Determines pattern and infiltration of hair loss |
| Blood Tests | Checks for deficiencies or hormonal imbalances | Identifies underlying health issues linked to hair loss |
| Pull Test | Several strands of hair are gently pulled to see how many come out | Evaluates the severity and stage of hair shedding |
If the first tests show a complex issue, more tests might be needed. These tests give a clearer picture. They lead to a precise diagnosis and a treatment plan that fits you.
Traditional and Emerging Treatments for Alopecia
Finding the right alopecia treatment can be tough. This part looks at old and new hair loss remedies and medical therapies for alopecia. It shows a wide range of choices for different levels of alopecia.
Corticosteroids are a key part of treating alopecia because they fight inflammation. They can be applied to the scalp, taken by mouth, or injected. But, using them for a long time can cause side effects. Doctors need to watch patients carefully.
New treatments like JAK inhibitors and Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) therapy are becoming popular. JAK inhibitors were first used for bone marrow diseases but help with alopecia areata. PRP therapy uses the patient’s own platelets to help hair grow. It’s a favorite because it’s natural and works well.
| Treatment | Type | Primary Benefit | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Traditional | Reduces inflammation | Skin thinning, acne |
| JAK Inhibitors | Emerging | Targets autoimmune response | Headaches, sensitive skin |
| PRP Therapy | Emerging | Enhances hair regrowth | Mild pain at injection site |
Looking into these alopecia treatment options is key for those dealing with hair loss. It’s important to talk to doctors to find the best treatment for each person.
Living with Alopecia: Coping Mechanisms and Support
Living with alopecia is more than just hair loss. It affects people emotionally and socially. It’s important to address the emotional side to offer full alopecia support.
Psychological Impact of Hair Loss and Finding Support
The journey of coping with hair loss can be tough. People may feel grief, stress, and loneliness. But, finding support from others who get it is key.
Joining alopecia support groups, online or in person, helps a lot. It’s a place to share stories and feel understood. This can make you feel less alone.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Alopecia
Changing your lifestyle can help manage alopecia better. This includes eating right, reducing stress, and finding gentle hair care. These changes can improve your life in many ways.
| Coping Strategy | Benefits | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Nutritional adjustments | Boosts overall health, may mitigate hair loss | Incorporate a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals |
| Mindfulness and meditation | Reduces stress, linked to severity of symptoms | Practice regularly to maintain mental well-being |
| Specialized hair care | Prevents further hair damage/scalp irritation | Use gentle products designed for sensitive scalp |
Managing alopecia is not just about treating hair loss. It’s about building a supportive lifestyle. This lifestyle should meet both the physical and emotional needs of the condition.
Success Stories: Overcoming the Challenges of Alopecia
Inspirational alopecia journeys offer hope and practical solutions for those dealing with hair loss. These stories show the strength and determination needed to thrive with alopecia. Chloe’s story, for example, shows how following the Autoimmune Protocol (AIP) diet can lead to significant improvements.
Many others have found ways to overcome hair loss, growing personally and finding empowerment. Some find relief in medical treatments, while others try alternative therapies or join support groups. These stories remind us of the human spirit’s strength and offer different ways to manage alopecia.
Knowing about the different types of alopecia and treatments is key to fighting hair loss. Education helps people make informed choices, giving them the tools for success. Whether through shared experiences or medical advice, those with alopecia have many resources to face their challenges. These stories show that beating hair loss is not just possible but can also bring strength and a renewed sense of well-being.
FAQ
Q: What is alopecia disease?
A: Alopecia is a term for hair loss. It includes different conditions that can cause partial or complete baldness. These include alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis, each with its own symptoms and hair loss patterns.
Q: What are the typical symptoms of alopecia?
A: Symptoms of alopecia can vary. They range from small hair loss patches to complete baldness or loss of all body hair. Early signs include hair falling out in clumps, a lot of hair shedding, and thinning hair.
Q: How common is alopecia?
A: Alopecia is quite common and can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. Millions of people worldwide have alopecia areata. It’s important to remember that hair loss is not rare.
Q: What causes alopecia?
A: Alopecia can be caused by genetics, autoimmune reactions, hormonal changes, and environmental factors. For example, alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles.
Q: What are the different types of alopecia?
A: There are several types of alopecia. These include alopecia areata (patchy hair loss), alopecia totalis (complete scalp hair loss), and alopecia universalis (loss of all body hair). There are also rarer forms like scarring alopecia, which causes permanent hair loss.
Q: How is alopecia diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis starts with a dermatologist’s physical examination. They look at the pattern of hair loss. Tests like scalp biopsies, blood tests, or pull tests may be done to confirm the type of alopecia and rule out other conditions.
Q: What treatments are available for alopecia?
A: Treatment options depend on the type and severity of alopecia. They include corticosteroid injections, topical treatments, oral medications like JAK inhibitors, light therapy, or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. However, some alopecia types are harder to treat, and results vary.
Q: Can lifestyle changes affect alopecia?
A: Lifestyle changes can’t cure alopecia but may improve hair health and reduce triggers. This includes managing stress, eating a balanced diet, and protecting the scalp from sun damage.
Q: How can someone cope with the psychological impact of alopecia?
A: Coping with alopecia’s emotional effects involves seeking support and considering counseling. Solutions like wigs or hairpieces can also help. Acceptance and community support are crucial in managing the emotional impact.
Q: Are there success stories of people overcoming alopecia?
A: Yes, many people have overcome alopecia. Success stories highlight the importance of support, persistence with treatments, and self-acceptance. These stories offer hope and encouragement to others facing alopecia.